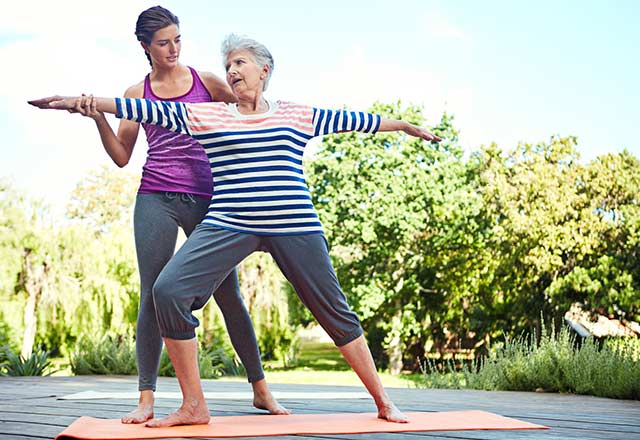
Physiotherapy for Parkinson’s Disease: Improving Movement and Independence
Introduction
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological condition that affects movement, balance, posture, and coordination. While there’s currently no cure, early and consistent physiotherapy can significantly slow down the progression of symptoms, help maintain mobility, and enhance quality of life.

What Is Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s disease is a chronic condition caused by the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain. Dopamine is essential for controlling smooth, coordinated movement. The exact cause is unknown, but both genetic and environmental factors may contribute.

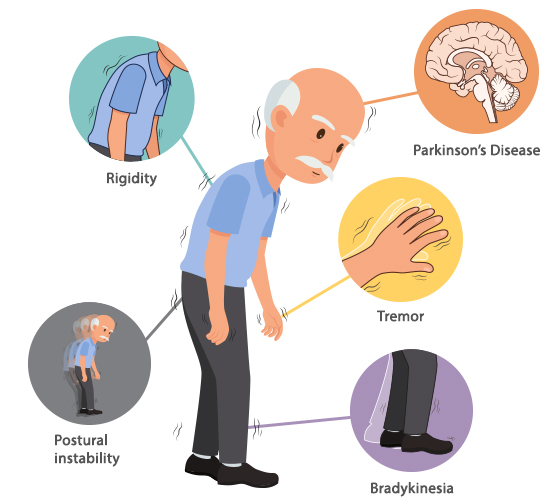
Common Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s can present a variety of symptoms, which tend to worsen over time:
- Tremors or shaking
- Muscle stiffness (rigidity)
- Bradykinesia (slowness of movement)
- Postural instability
- Shuffling gait or reduced arm swing
- Freezing episodes (sudden inability to move)
- Balance difficulties
- Soft speech or facial masking
These symptoms interfere with daily activities, making physiotherapy an essential part of managing the condition.

Integrating Physiotherapy and Cognitive Training in Parkinson’s Disease Management: A Case Study Overview
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder marked by the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, leading to hallmark motor impairments such as tremors, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. Beyond motor deficits, PD also affects cognitive function, resulting in memory impairment, executive dysfunction, and difficulties with attention, which collectively diminish quality of life (QOL). While pharmacological therapies provide symptomatic relief, their effect on long-term functional recovery and cognitive outcomes is limited, highlighting the need for complementary non-pharmacological strategies. ( Source: https://bfpt.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s43161-025-00286-y)
This case report explores the physiotherapy management of a 72-year-old male with stage 3 PD, illustrating the impact of a 14-week intensive, individualized physiotherapy program integrating balance, coordination, strength, aerobic conditioning, and cognitive training.
Patient Profile and Baseline Assessment
The patient, B.R., presented with progressive bilateral tremors, postural instability, and moderate cognitive impairment (MMSE score: 17). Functional assessments revealed a Berg Balance Scale (BBS) score of 30, Timed Up and Go (TUG) time of 16 s, and a 6-Minute Walk Test (6MWT) completion of 16 laps. Tremor frequency was significant (Rt UL: 90 tpm, Lt UL: 60 tpm), and his PDQ-39 score indicated moderate impairment in activities of daily living and overall QOL. Hoehn and Yahr classification was stage 3, reflecting moderate motor disability.
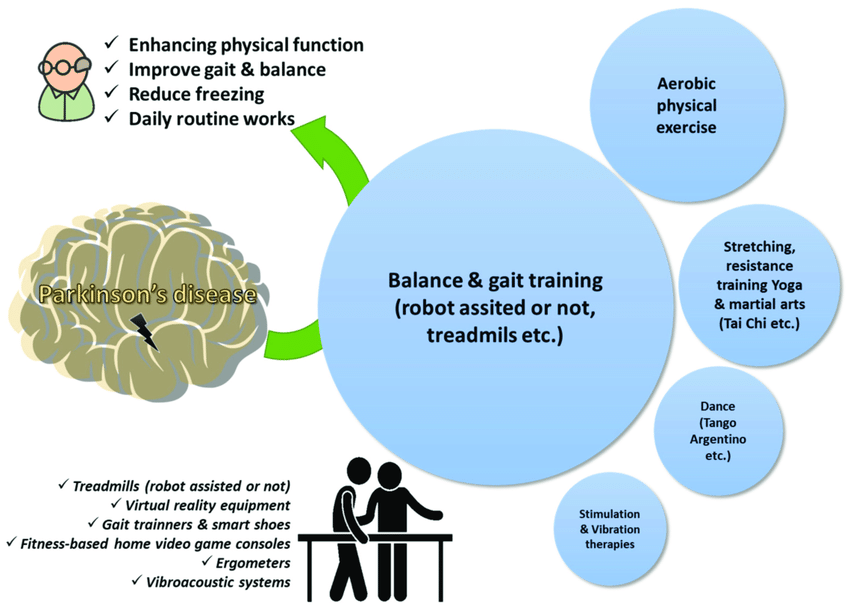
Physiotherapy Intervention
The intervention program was multimodal, structured to target both motor and non-motor PD symptoms:
- Postural Training, Balance, and Coordination
- Core stabilization and extensor muscle exercises addressed stooped posture and postural instability.
- Swiss ball perturbation exercises and tandem walking improved static and dynamic balance and proprioception.
- Fine motor coordination drills, including rapid finger-to-thumb taps and pronation/supination sequences, reduced tremor amplitude and enhanced upper-limb dexterity.
- Aerobic, Strength, and Resistance Training
- Low-impact aerobic exercises (bicycle ergometry, 6MWT) enhanced cardiovascular endurance and functional mobility.
- Strength and resistance exercises focused on postural and antigravity muscles, incorporating squats, sit-to-stand drills, and tandem walking with progressive weights.
- Low-resistance, high-repetition protocols mitigated rigidity while promoting muscular endurance and postural stability.
- Functional Mobility and Cognitive Training
- Task-specific movements, such as simulated transfers and stair climbing, reinforced daily functional independence.
- Cognitive interventions, including serial subtraction, symbol-word tracking, and mental sequencing, targeted working memory, attention, and executive function.
- Exercise Progression and Fatigue Management
- Interval-based training with alternating activity and rest periods minimized fatigue and ensured cardiovascular safety.
- Progressive exercise volumes and intensity, monitored via vital signs and functional tolerance, enabled safe adaptation to increasing physical and cognitive demands.
- Home Exercise Program
- A supplementary regimen reinforced clinic-based gains in balance, postural control, and cognitive engagement, promoting continuity and sustainability of improvements.
Outcomes and Results
Following the 14-week intervention, B.R. demonstrated substantial improvements:
- Motor Function: BBS increased to 41; TUG reduced to 12 s; 6MWT laps increased to 24; tandem walk time improved from 42 s to 26 s. Tremor frequency decreased from severe to minimal, and TETRAS score improved from 11 to 5. Hoehn and Yahr stage improved from 3 to 1, indicating minimal motor impairment.
- Cognitive Function: MMSE improved from 17 to 23, with enhancements in attention, working memory, and executive function.
- Quality of Life: PDQ-39 score decreased from 45% to 18%, reflecting improved independence, mobility, and emotional well-being.
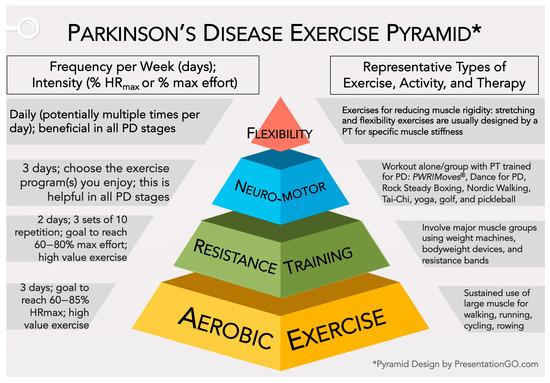
Discussion
This case highlights the synergistic impact of integrating physiotherapy with cognitive rehabilitation in PD management. Structured postural, balance, and coordination exercises facilitate neuroplasticity and improve anticipatory postural adjustments, critical for stability. Aerobic and resistance training enhance cardiovascular fitness, muscular endurance, and functional mobility, mitigating bradykinesia and rigidity. Cognitive exercises reinforce fronto-striatal circuits, improving attention, memory, and executive function, which are often impaired in PD.
Evidence from prior studies supports these findings, emphasizing that intensive, individualized, non-pharmacological interventions can significantly improve motor and cognitive outcomes in PD, even in advanced stages. This approach offers a holistic management strategy, addressing both the physical and cognitive dimensions of the disease.
Limitations and Future Directions
- Single-case design limits generalizability.
- Concurrent pharmacological treatment complicates attribution of outcomes solely to physiotherapy.
- Short duration limits insights into long-term sustainability of improvements.
Future studies should incorporate larger patient cohorts, multicenter trials, and longitudinal follow-ups to validate and optimize physiotherapy protocols for PD.
How Can Physiotherapy Help Parkinson’s Patients?
Physiotherapy helps people with Parkinson’s by:
- Improving mobility and flexibility
- Enhancing balance and coordination
- Building muscle strength
- Correcting posture
- Addressing gait issues like shuffling or freezing
- Boosting confidence in daily movements
At FitoFine, our therapy plans are tailored to the individual’s stage, whether early, middle, or advanced Parkinson’s.

Key Goals of Parkinson’s Physiotherapy
- Restore and maintain functional movement
- Improve independence in daily life
- Prevent complications like joint stiffness or falls
- Support cognitive and emotional well-being through movement
Our 5-Step Physiotherapy Approach at FitoFine
1. Comprehensive Assessment
We begin with a thorough evaluation of:
- Balance and gait patterns
- Muscle strength and flexibility
- Joint range of motion
- Posture and coordination
- Ability to perform daily tasks
This helps us develop a personalized treatment plan.
2. Exercise-Based Interventions
A. Mobility Exercises
- Stretching tight muscles
- Strengthening weak areas
- Improving joint range of motion
B. Balance and Coordination Training
- Standing on one foot
- Tandem (heel-to-toe) walking
- Navigating obstacles
- Using balance boards
C. Gait Training
- Visual/auditory cueing (lines on the floor, metronomes)
- Treadmill walking with harness support
- Stride length and arm swing retraining
D. Postural Correction
- Core muscle activation
- Techniques to reduce stooping posture
- Spinal alignment exercises
E. Dual Task Training
- Combining movement with cognitive tasks
- Enhancing brain-body coordination
3. Fall Prevention Strategies
- Educating on the safe use of walking aids
- Training in safe turning, transferring, and navigation
- Home safety evaluations and suggestions
4. Breathing and Voice Support
Later-stage Parkinson’s can impact speech and breathing. Our plan includes:
- Diaphragmatic breathing
- Chest expansion techniques
- Movement-breath coordination
5. Functional Training
Helping patients regain control over daily routines:
- Getting in and out of bed
- Standing from a chair
- Climbing stairs
- Dressing and grooming
Importance of Early Physiotherapy in Parkinson’s
Starting physiotherapy early in the diagnosis can delay the onset of severe symptoms. It helps patients:
- Retain functional independence longer
- Learn compensatory strategies early
- Reduce the emotional burden of disease progression

Home Exercise Programs
Our support continues beyond clinic visits. We offer customized home routines, including:
- Walking schedules
- Chair and balance exercises
- Cue-based movement strategies
- Safety tips for caregivers and families
Why FitoFine Is the Right Choice for Parkinson’s Physiotherapy
Here’s what makes us different:
- Neuro-physiotherapy experts with Parkinson’s specialization
- Evidence-based, progressive treatment plans
- Compassionate, one-on-one care
- Clean, calming clinical setup
- Evening sessions are ideal for working families
- Family education and involvement in care plans
FAQs About Parkinson’s Physiotherapy
Q1: Can physiotherapy cure Parkinson’s disease?
No, but it can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Q2: When should therapy begin?
As early as possible. Early intervention slows disease progression and maintains mobility.
Q3: How often should I attend sessions?
We recommend 2–3 sessions per week initially, depending on your condition.
Q4: Is physiotherapy suitable for elderly patients?
Absolutely. Even seniors in advanced stages benefit from guided therapy and movement education.
Q5: What if travel is difficult for the patient?
FitoFine offers home-based exercise plans and online consultation support for patients unable to visit in person.
Book Your Parkinson’s Physiotherapy Session Today!
Take back control of your movement and regain your confidence. At FitoFine Physiotherapy Clinic, we walk with you, literally and figuratively, on the path to better mobility. This case underscores the critical role of physiotherapy as a non-pharmacological intervention in Parkinson’s disease, demonstrating that a structured, intensive program targeting both motor and cognitive deficits can substantially enhance functional independence, tremor control, and overall QOL.
Early integration of such interventions into PD management may facilitate neuroplasticity, mitigate disease progression, and provide a robust, holistic approach to patient care.
Timings: Monday to Saturday – 5:00 PM to 10:00 PM | Sunday – Closed
Phone: +91 6295115701
Email: fitofine.in@gmail.com
Website: www.fitofine.com
Stay strong, stay steady. FitoFine is here for your Parkinson’s journey.


